Have you ever sat in a meeting with a field foreman, production engineers, chemical engineers, and landmen? Have you ever been lost with all the jargon and verbiage thrown around in the room or even out in the field? I HAVE!
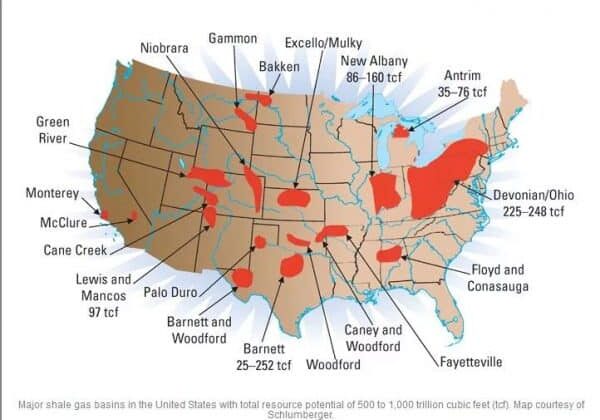
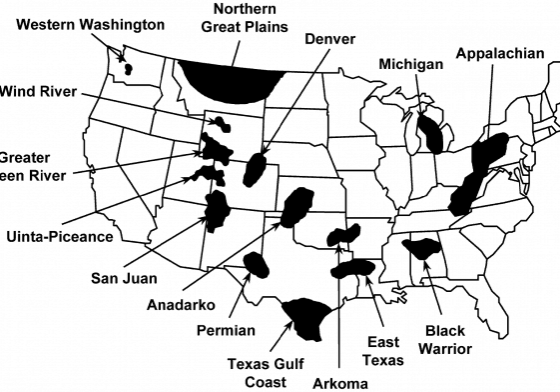
After over two years in the industry, I still come across new terms or slang terms on a regular basis…I have even learned that there is a huge difference between the terms used in each region of America for the same thing. Did you know a “salt bed” is the same as a “dehy”? I learned that about six months ago…and that’s because we have a service region in the Marcellus Shale play. If CROFT had no location in the North, I might still be in the dark about “salt beds”.
To ensure this does not happen to you, I made up a list…are there any terms you have come across that you didn’t know? Do you have any terms that are not listed here but should be listed here? Tell me- I will develop a part 2 for this article!
Abandon– (1) The proper plugging and abandoning of a well in compliance with all applicable regulations and the cleaning up of the well site to the satisfaction of any governmental body having jurisdiction with respect thereto and to the reasonable satisfaction of the operator.(2) To cease efforts to find or produce from a well or field. (3) To plug a well completion and salvage material and equipment.
Abandoned well– well no longer in use; a dry hole that, in most cases, must be properly plugged.
Absorption– a process used by older gas processing plants and in many refinery gas plants to remove natural gas liquids from natural gas. The gas is run through oil of a proper character that absorbs the liquid components of the gas. This process is not as efficient as cryogenic processing, and only 70% propane and all of the butane and natural gasoline are recovered.
Amine– Organic base used in refining operations to absorb acidic gases (H2S, COS, CO2) occurring in process streams. Two common amines are monoethanolamine (MEA) and diethanolamine (DEA).
Amine unit– A natural gas treatment unit for using amines to remove contaminants (H2S, COS, CO2). Amine units are often skid-mounted so they can be moved to the site of new gas production. Gas containing H2S and other impurities must be cleaned up before it is acceptable to gas transmission pipelines. (GSS) Gas Sweetening System
Annulus-The space between (1) The casing and the wall of the borehole.(2) Two strings of casing.(3) Tubing and casing.
API– API, or the American Petroleum Institute, is a standards-setting institute with over 700 standards for operational and environmental safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
Artificial Lift– Pumping an oil well with a rod, tubing, or bottom-hole centrifugal pump may be termed artificially lifting crude oil to the surface or doing so by mechanical means.
Associated Gas-A well drilled as part of an appraisal drilling program which is carried out to determine the physical extent, reserves and likely production rate of a field.
Barrel– A unit of volume measurement used for petroleum and its products (7.3 barrels = 1 ton: 6.29 barrels = 1 cubic meter).
Basket price-The blanket or average price of crude oil on the world market. For example, the basket price of $18.00/bbl. could mean the average price of average gravity. Lower-gravity crude with high-transit cost would bring less than $18.00. Conversely, higher gravity crude with low sulfur and close to market would be a premium – a basket of crude oils of differing gravities, sulfur content, sweet and sour. Read an article on the difference between all the oil pricing.
Blow-out preventers (BOPs) – These are high-pressure wellhead valves designed to shut off the uncontrolled flow of hydrocarbons.
Bullet tanks- horizontal pressure tanks that are the shape of a very fat bullet. Bullet tanks are used to store normal butane, propane, and propylene.
Casing – Pipe cemented in the well to seal off formation fluids or keep the hole from caving in.
Downhole – A term to describe tools, equipment, and instruments used in the well bore; also conditions or techniques applying to the well bore.
E&A – Abbreviation for Exploration and Appraisal.
E&P – Abbreviation for Exploration and Production
Exploration – A general term referring to all efforts made in the search for new deposits of oil and gas.
Flaring – A term for burning off natural gas in a controlled manner whether for safety reasons or removal of excess natural gas. Environmental standards are reducing and regulating flaring across the industry.
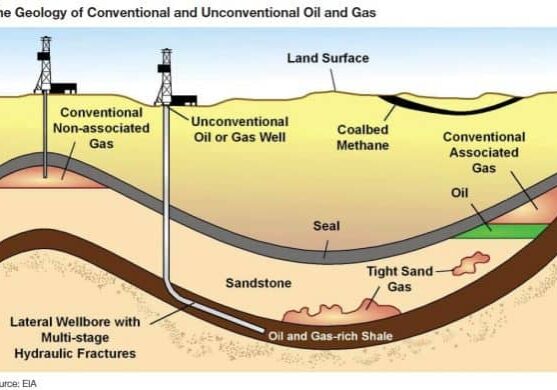
Fracturing – A method of breaking down a formation by pumping fluid at very high pressures. The objective is to increase production rates from a reservoir. What is fracking?
Hydrocarbon– A compound containing only the elements hydrogen and carbon. May exist as a solid, a liquid or a gas. The term is mainly used in a catch-all sense for oil, gas and condensate.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) – Oilfield or naturally occurring gas, chiefly methane, liquefied for transportation.
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) – Light hydrocarbon material, gaseous at atmospheric temperature and pressure, held in the liquid state by pressure to facilitate storage, transport and handling. Commercial liquefied gas consists essentially of either propane or butane, or mixtures thereof.
mmcfd– Millions of cubic feet per day (of gas).
Pipeline gas– Gas under sufficient pressure to enter the high-pressure gas lines of a purchaser; gas sufficiently dry so that liquid hydrocarbons – natural gasoline, butane, and other gas liquids usually present in natural gas – will not condense or drop out in the transmission lines.
Pipelines – a tubular arrangement for transmitting crude oil, refined products, and natural gas from the wellhead, refinery, and storage facility to the customer. The pipeline measures 14 to 42 inches in diameter but is usually 20 to 36 inches. It is often composed of 40-foot lengths, which may be as long as 60 or 80 feet. The pipe is wrapped and coated for protection against corrosion, especially since it runs underground. About half of all gas and oil is moved by pipeline.
Pigging – is the practice of pipeline maintenance that involves sending a device called a “pig” to clean or inspect the pipeline.
Refinery– a large plant composed of many different processing units that convert crude oil into finished or refined products. These processes include heating, fractionating, reforming, cracking, and hydrotreating.
Refrigeration – the process used to remove the natural gas liquids by cooling or refrigerating the natural gas until the liquids are condensed out. The plants use Freon or propane to cool the gas.
Soap sticks – Soap sticks are surfactants that assist in gas production by creating a foam head that releases water and condensates from the well.
Sweet gas– Natural gas free of significant amounts of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) when produced.
Unassociated gas – Natural gas occurring alone, not in solution, or as free gas with oil or condensate.
Workover – Remedial work to the equipment within a well, the well pipework, or relating to attempts to increase the flow rate.